# Magenta MIDI Interface
This interface allows you to connect to a model
[generator](/magenta/models/README.md#generators) via a MIDI controller
and synthesizer. These can be either "hard" or "soft" components.
Note that you can only interface with a trained models that have a
[SequenceGenerator](/magenta/music/sequence_generator.py)
defined for them.
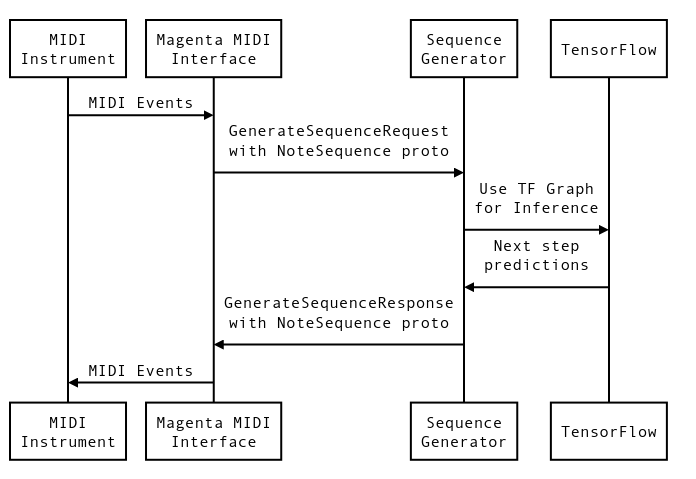
## Installing Dependencies
Before using the interface, you will need to install some
dependencies. We have provided instructions for both Macintosh OS X
and Ubuntu Linux.
For users of Macintosh OS X, the instructions below assume that you
have installed [Homebrew](http://brew.sh).
### Install PortMidi
The interface uses a python library called [mido](http://mido.readthedocs.io) to
interface your computer's MIDI hub. For it to work, you need to separately
install a backend library it can use to connect to your system. The easiest to
install is PortMidi, which can be done with the following commands.
**Ubuntu:** `sudo apt-get install libportmidi-dev`
**Mac:** `brew install portmidi`
### Install QjackCtl (Ubuntu Only)
[QjackCtl](http://qjackctl.sourceforge.net/) is a tool that provides a graphical
interface for the JACK hub on Ubuntu to allow you to easily route signals
between MIDI components. You can install it using `sudo apt-get install
qjackctl`.
### Connect/Install MIDI Controller
If you are using a hardware controller, attach it to the machine. If you do not
have one, you can install a software controller such as
[VMPK](http://vmpk.sourceforge.net/) by doing the following.
**Ubuntu:** Use the command `sudo apt-get install vmpk`.
**Mac:** Download and install from the
[VMPK website](http://vmpk.sourceforge.net/#Download).
### Connect/Install MIDI Synthesizer
If you are using a hardware synthesizer, attach it to the machine. If you do not
have one, you can install a software synthesizer such as [FluidSynth]
(http://www.fluidsynth.org) using the following commands:
**Ubuntu:** `sudo apt-get install fluidsynth`
**Mac:** `brew install fluidsynth`
If using FluidSynth, you will also want to install a decent soundfont. You can
install one by doing the following:
**Ubuntu:** Use the command `sudo apt-get install fluid-soundfont-gm`.
**Mac:** Download the soundfont from
http://www.musescore.org/download/fluid-soundfont.tar.gz and unpack the SF2
file.
## Set Up
### Ubuntu
Launch `qjackctl`. You'll probably want to do it in its own screen/tab
since it will print status messages to the terminal. Once the GUI
appears, click the "Start" button.
If using a software controller, you can launch it in the background or in its
own screen/tab. Use `vmpk` to launch VMPK.
If using a software synth, you can launch it in the background or in its own
screen/tab. Launch FluidSynth with the recommended soundfont installed above
using:
```bash
$ fluidsynth /usr/share/sounds/sf2/FluidR3_GM.sf2
```
In the QjackCtl GUI, click the "Connect" button. In the "Audio" tab, select your
synthesizer from the list on the left (e.g., "fluidsynth") and select "system"
from the list on the right. Then click the "Connect" button at the bottom.
### Mac
If using a software controller (e.g., VMPK), launch it.
If using a software synth, launch it. Launch FluidSynth with the
recommended soundfont downloaded above using:
```bash
$ fluidsynth /path/to/sf2
```
## Launching the Interface
After completing the installation and set up steps above, build the interface
with:
```bash
$ bazel build //magenta/interfaces/midi:magenta_midi
```
Once built, have it list the the available MIDI ports:
```bash
$ bazel-bin/magenta/interfaces/midi/magenta_midi --list
```
You should see a list of available input and output ports, including both the
controller (e.g., "VMPK Output") and synthesizer (e.g., "FluidSynth virtual
port").
To use the midi interface, you can use either a pre-trained model bundle or a
checkpoint.
### Pre-trained bundle
To use a pre-trained bundle, first download the bundle .mag file. There are
links to bundle files on each of our model pages (e.g.,
[Basic RNN](/magenta/models/basic_rnn/README.md),
[Lookback RNN] (/magenta/models/lookback_rnn/README.md),
[Attention RNN] (/magenta/models/attention_rnn/README.md), etc.).
You can now start the interface with this command, supplying the location of the
.mag bundle file:
```bash
$ bazel-bin/magenta/interfaces/midi/magenta_midi \
--input_port= \
--output_port= \
--bundle_file=
```
Assuming you're using the
[Attention RNN](/magenta/models/attention_rnn/README.md) bundle file and are
using VPMK and FluidSynth, your command would look like this:
```bash
$ bazel-bin/magenta/interfaces/midi/magenta_midi \
--input_port="VMPK Output" \
--output_port="FluidSynth virtual port" \
--bundle_file=/tmp/attention_rnn.mag
```
### Training checkpoint
This method assumes you have already trained a model with a
[generator](/magenta/models/README.md#generators) defined for it
(e.g., [Basic RNN](/magenta/models/basic_rnn/README.md),
[Lookback RNN] (/magenta/models/lookback_rnn/README.md),
[Attention RNN] (/magenta/models/attention_rnn/README.md), etc.).
You can now start the interface with this command, supplying the same
hparams you used when you trained the model:
```bash
$ bazel-bin/magenta/interfaces/midi/magenta_midi \
--input_port= \
--output_port= \
--generator_name= \
--checkpoint= \
--hparams=
```
Assuming you trained the
[Attention RNN](/magenta/models/attention_rnn/README.md) and are
using VPMK and FluidSynth, your command would look like this:
```bash
$ bazel-bin/magenta/interfaces/midi/magenta_midi \
--input_port="VMPK Output" \
--output_port="FluidSynth virtual port" \
--generator_name=attention_rnn \
--checkpoint=/tmp/attention_rnn/logdir/run1/train \
--hparams="{'batch_size':64,'rnn_layer_sizes':[64,64]}"
```
## Using the Interface
To initialize a capture session, you need to send the appropriate control change
message from the controller. By default, this is done by setting the modulation
wheel to its max value.
You should immediately hear a metronome and the keys will now produce sounds
through your audio output.
When you have played your priming sequence, end the capture session by sending
the appropriate control change message from the controller. By default, this is
done by setting the modulation wheel back to 0.
After a very short delay, you will hear the input sequence followed by the
generated sequence. You can continue to switch between capture and generating
states using the appropriate control (e.g., the modulation wheel).
## Changing the Capture/Generate Toggle
You can remap the control signals to use something other than the modulation
wheel (e.g., physical pads on your controller). This is done by setting the
`--start_capture_control_*` and `--stop_capture_control_*` flags appropriately.

